Jingyu Hu 鲸鱼湖
Qinghai | Northwest China
Date of acquisition: 14 November, 2025 | 04:52:31 UTC/p>
Sensors: Sentinel-2A L1C
Coordinates: ca. 36.3°N, 89.4°E
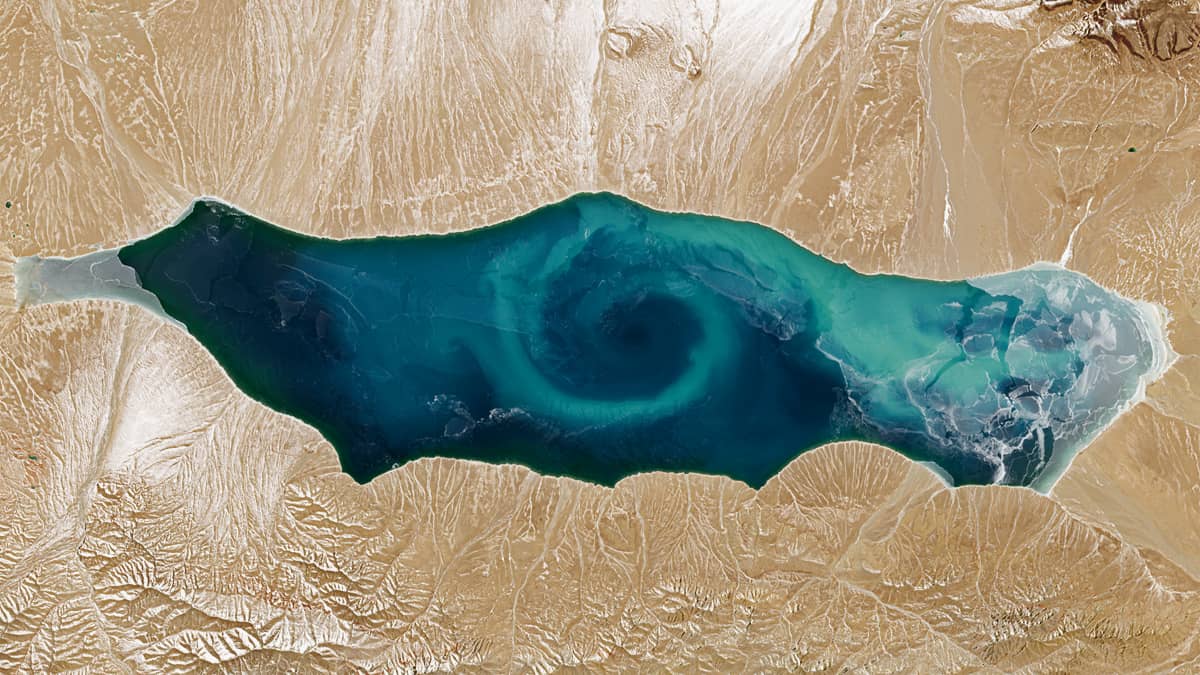
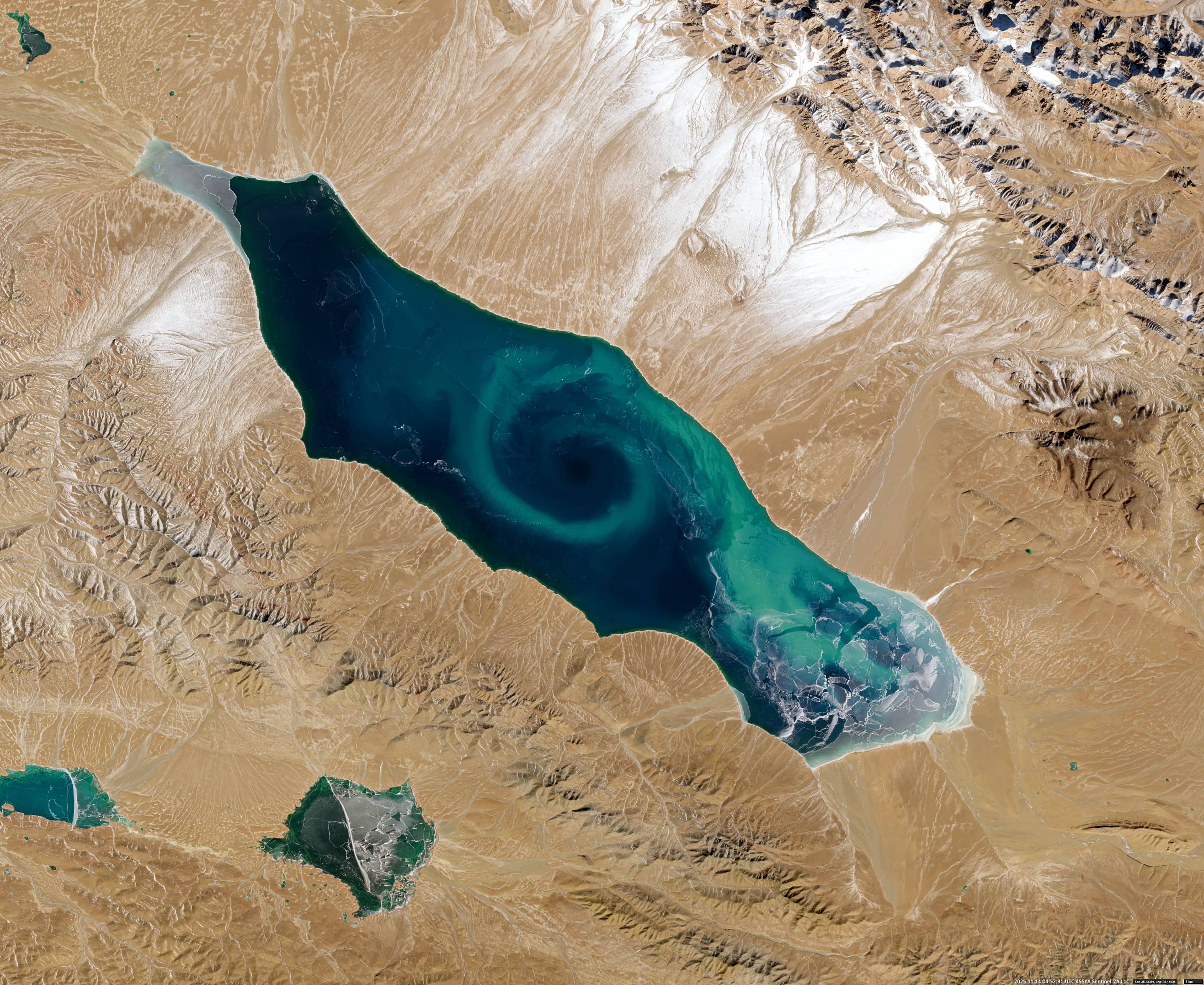
The high altitude salt lake Jingyu Hu (鲸鱼湖, also known as Whale Lake) is located in the Altun Mountains Nature Reserve (阿尔金) on the border of Xinjiang with Tibet and Qinghai. Lying at an altitude of 4,713 meters, it is fed by meltwater from snow and glaciers. The lake covers an area of approximately 415 km² and ranges in depth from 2 to 20 meters.
Whale Lake is the last mountain lake in China to be mapped. This was achieved using satellite remote-sensing data, which was then confirmed by subsequent field expeditions. The lake’s name derives from its morphology, which resembles the outline of a whale.
The eastern part of the lake has comparatively low salinity due to significant glacial meltwater inflow from the Yulang River (玉浪河), and supports a higher concentration of plankton. In contrast, the western part has no significant freshwater inflow, is subject to intense evaporative processes and approaches saturation salinity, resulting in a hypersaline, stagnant and largely abiotic environment. Due to this pronounced spatial heterogeneity, Jingyu Hu is also called “Yin-Yang Lake.”
The area around the lake is considered an internationally significant biodiversity hotspot.
The lake is usually ice-free from late June to late November. During this period, satellite observations often reveal a large vortex of planktonic biomass and suspended sediments in the centre of the lake that extends almost the entire width. These vortices vary in chromatic intensity and particle concentration. The vortex structure is particularly clearly visible in the image shown. We can even see the water colour and its patterns below the partly transparent to semi-transparent ice, which makes the images even more special.
Further reading
Jingyu, Lake (Database for Hydrological Time Series of Inland Waters (DAHITI))
Key Biodiversity Areas




