Nioghalvfjerdsbræ
Northeast Greenland
Dates of acquisition:
• 2025.09.03 | 15:48:31 UTC
• 2025.08.29 | 15:38:31 UTC
Sensors: Sentinel-2A L2A
Coordinates: ca. 78.966°N, 25.609°W
The Northeast Greenland Ice Stream (NEGIS) is the main route by which ice from the northeastern part of the Greenland Ice Sheet flows into the North Atlantic.
Nioghalvfjerdsbræ, also known as the “79°N Glacier”, is the largest glacier flowing into the sea from the NEGIS and is the largest remaining ice shelf in the Arctic. It is located in King Frederik VIII Land. Situated west of Lamberts Land Island, it forms the southern arm of Zachariae’s Isstrøm (BC Earth Gallery).
While the 79°N glacier has remained relatively stable in the past, recent observations indicate an increase in surface flow and thinning of the glacier. These changes are assumed to be caused by atmospheric and ocean warming.
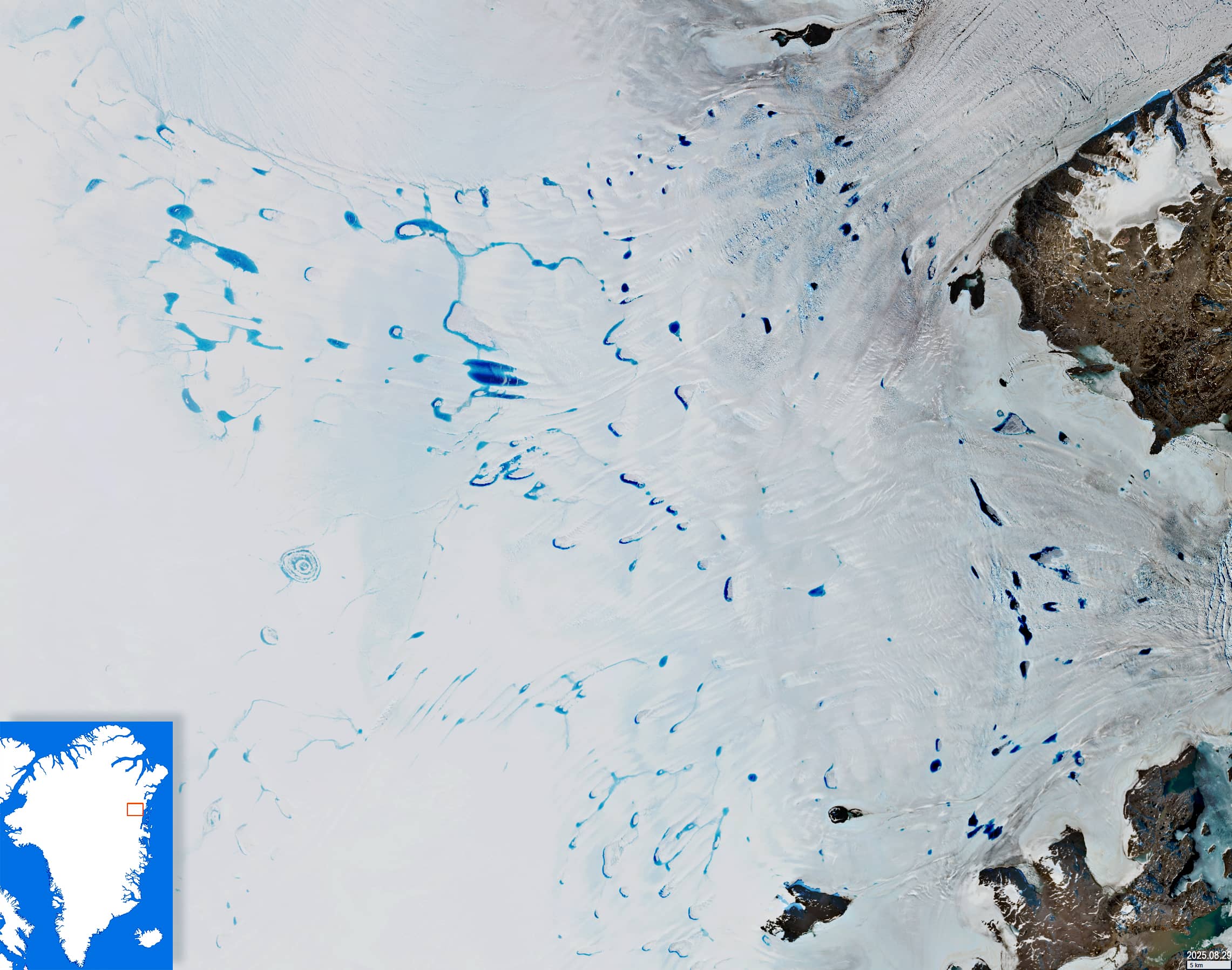
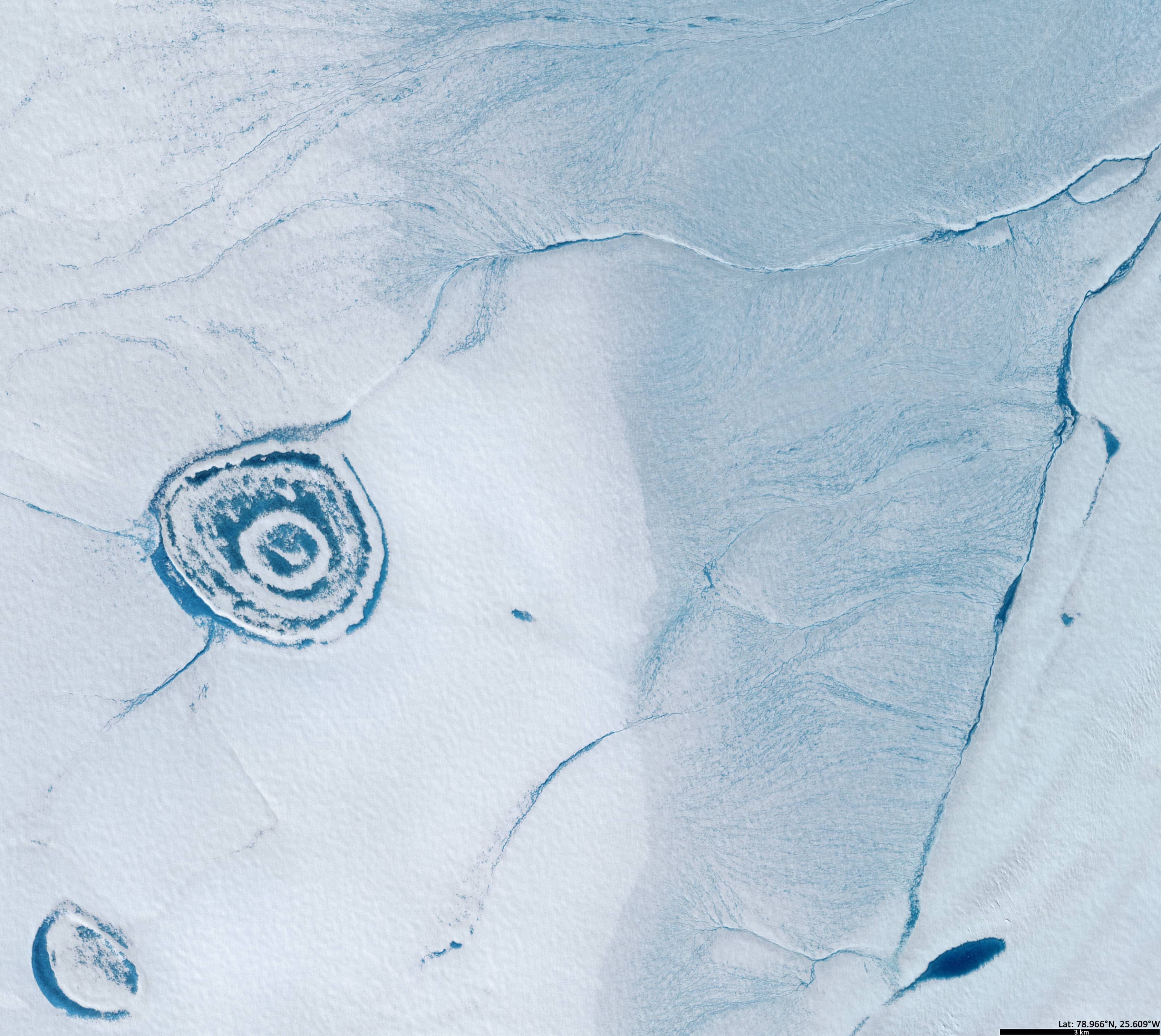
Approximately where the Greenland Ice Sheet merges with the 79°N Glacier, there is a large accumulation of supraglacial lakes, rivers, and channels (Figure 1).
Supraglacial lakes in Greenland are hydrological formations where glacial meltwater collects. Their existence leads to a decrease in surface albedo, which intensifies melting further. Surface meltwater can penetrate the subglacial drainage system through glacial mills, which are -vertical, almost circular shafts. This results in the transfer of fresh water from the glacier’s surface to its base and further into the ocean. Most of the lakes have a long lifespan: they can already be seen in various shapes on Sentinel-2 images from 2017 (for example, Figure 3).
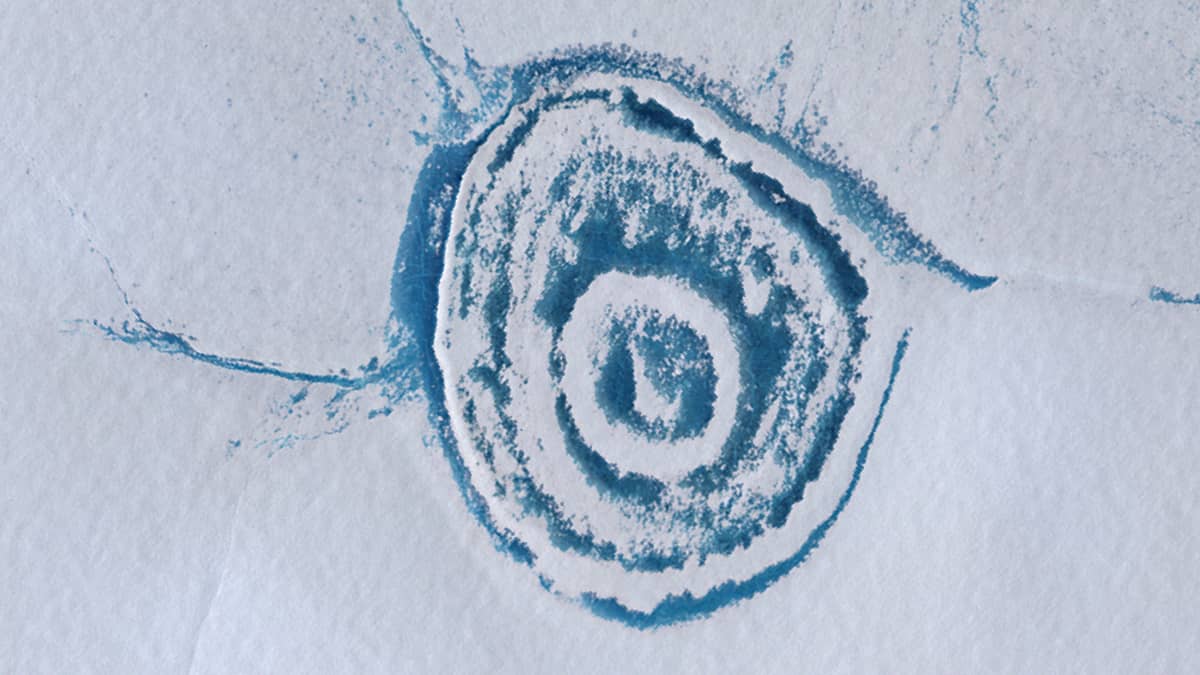
One lake (4.5 km × 4 km) stands out among the others in the region, resembling an onion in its outline (Figure 2). Its surface consists of several concentric circles of ice and open water. Two rivers flow into it from the west and southwest, while a small stream flows out of it in the northeast.
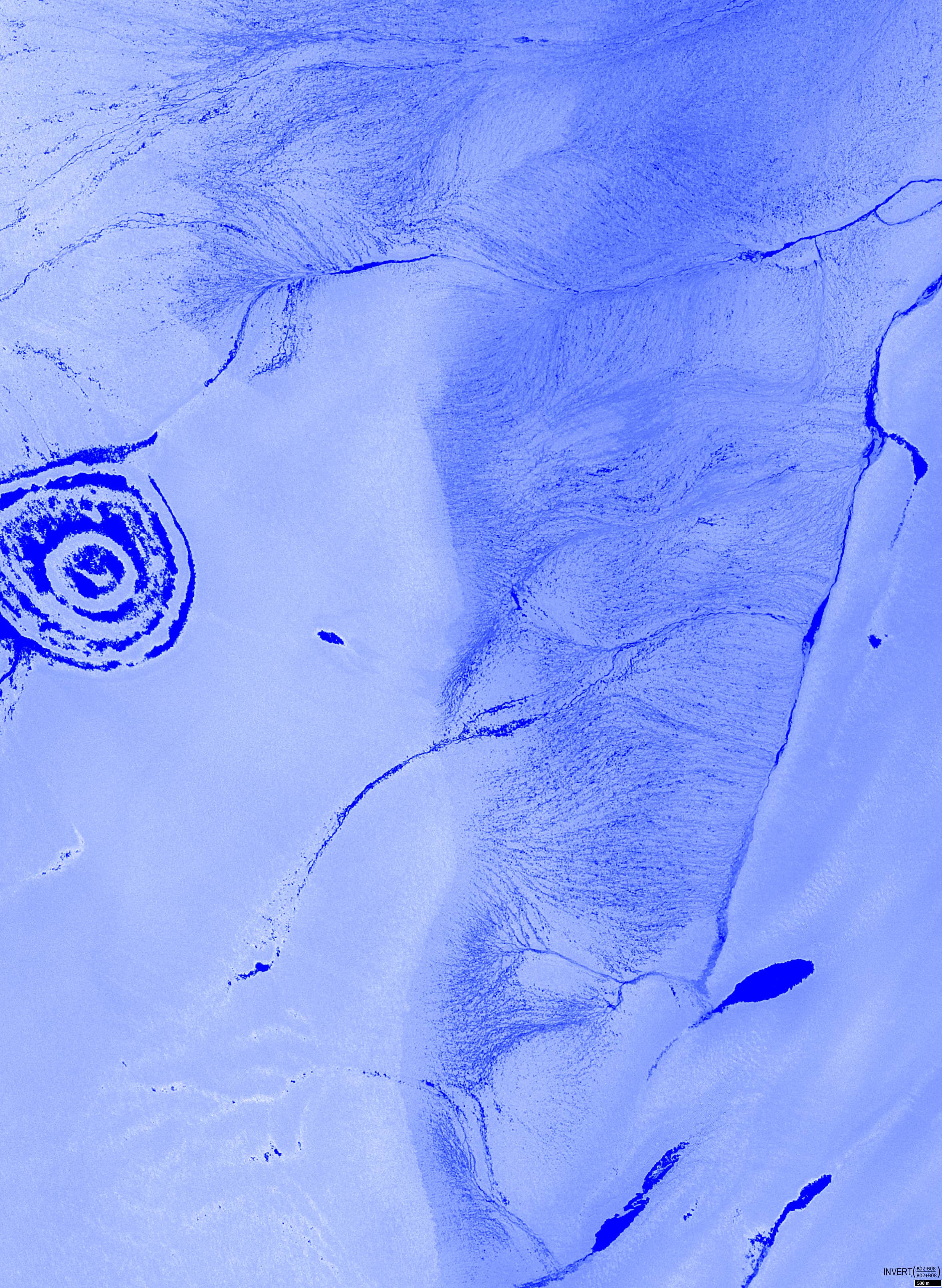
Figure 4 shows a band combination of bands called NDWI (normalized difference water index), which combines the near infrared and green bands:\( \frac{B3 – B8}{B3 + B8} \). This index visualises the impressive interconnected system of rivers, streams, and channels located at a lower elevation to the east of the “Onion Lake”.
Further reading
Nioghalvfjerdsfjorden (Wikipedia)
Nioghalvfjerdsbræ (Wikipedia)
Glacial stream (Wikipedia)
Zachariæ Isstrøm (Wikipedia)
Supraglacial lake (Wikipedia)