
| Level 3 Binning Operator | 
|
Using the I/O Parameters tab, the input products can be set, as well as the target product's name and target directory. See the screenshot below.
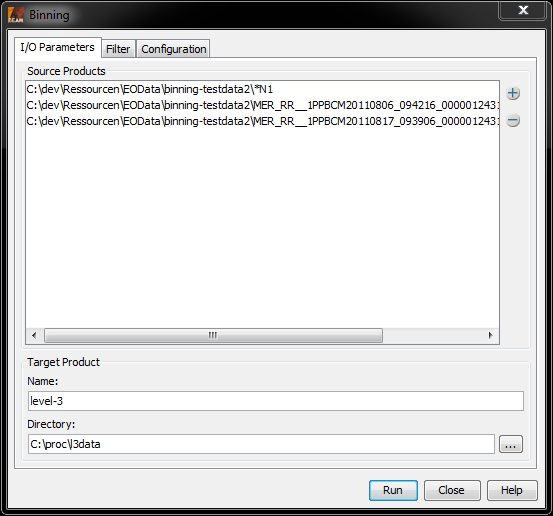
When the Run-button is clicked, the binning is performed according to the preferences that are specified in the "Filter-" and the "Configuration"-tabs.
Two filters can be applied to limit the contents of the target product. See the screenshot below for the user interface for the filters.
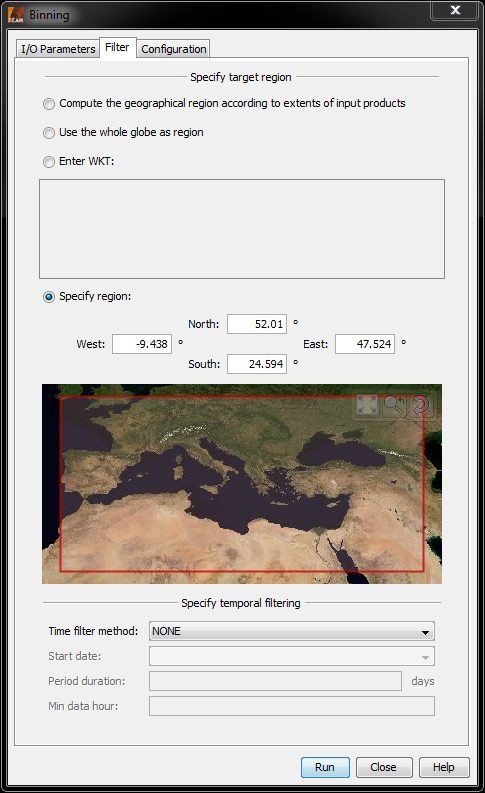
The target region filter can be used to set the bounds of the target product. It is able to operate in four different modes:
The method that is used to decide which source pixels are used with respect to their observation time.
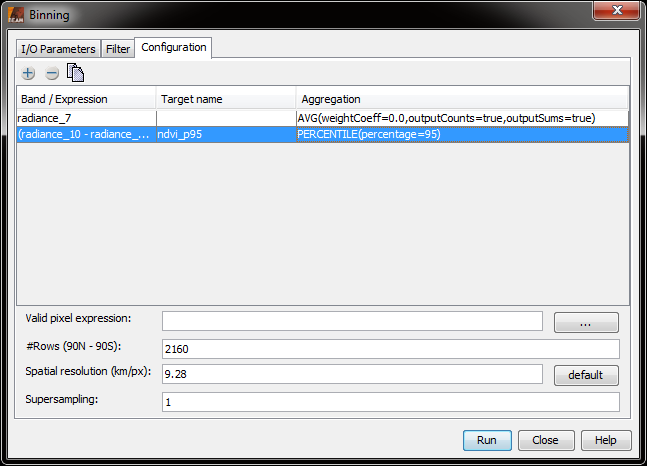
Using the table, the user can specify the sources that shall be aggregated for the target product. Using the plus and
minus buttons, sources (which can be any raster data, or expressions) can be added and removed.
The second column allows the user to set a target name for the aggregation; in case an expression is defined as
source, setting a target name is mandatory.
The third column is used to set the aggregation method; depending on which aggregation method is chosen, a number of
additional parameters must be set.
Table cells are edited via double click.
Using the valid expression, the user can specify which values in the source products shall be considered. Thus, a
boolean expression has to be set here. In the configuration of the example screenshot, only pixels that are not over
land are considered.
The target height of the source product may be set, too; this value has direct influence on the spatial resolution.
As long as the area of an input pixel is small compared to the area of a bin, a simple binning is sufficient. In this case, the geodetic center coordinate of the Level 2 pixel is used to find the bin in the Level 3 grid whose area is intersected by this point. If the area of the contributing pixel is equal or even larger than the bin area, this simple binning will produce composites with insufficient accuracy and visual artifacts such as Moiré effects will dominate the resulting datasets.
The following figure illustrates this problem.
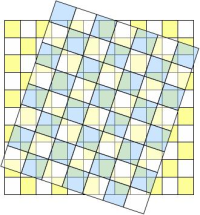
Level 2 grid (blue) and Level 3 grid (yellow)
The blue chessboard grid refers to the input data, the yellow one refers to the final Level 3 grid. As the figure clearly shows, single Level 2 pixels cannot be uniquely be assigned to single bins.
Supersampling parameter can be used to reduce or avoid the Moiré effect. The Moiré effect usually occurs when the spatial resolution used for the binning is similar to or smaller than the input pixel resolution. The supersampling subdivides every input pixel to n x n subpixels which all have the same values but different and unique geographical coordinates. This way, an input pixel may be distributed to more than one adjacent bin cell.